|
|
(C) Create CAdES p7m using AWS KMS to Sign in the Cloud
Demonstrates how to create a CAdES p7m, using AWS KMS. The signing of the hash happens in the Cloud on AWS KMS. Everything else regarding the creation of CAdES happens locally within Chilkat.
Note: This example requires Chilkat v9.5.0.96 or greater.
#include <C_CkCert.h>
#include <C_CkJsonObject.h>
#include <C_CkCrypt2.h>
void ChilkatSample(void)
{
HCkCert cert;
BOOL success;
HCkJsonObject jsonAwsKms;
HCkCrypt2 crypt;
HCkJsonObject signedAttrs;
const char *inputXmlPath;
const char *outputP7mPath;
// This example assumes the Chilkat API to have been previously unlocked.
// See Global Unlock Sample for sample code.
// Load the certificate used for signing. The certificate's private key is stored in AWS KMS
// However, we still need the certificate locally (without private key).
cert = CkCert_Create();
success = CkCert_LoadFromFile(cert,"qa_data/certs/myCert.cer");
if (success == FALSE) {
printf("%s\n",CkCert_lastErrorText(cert));
CkCert_Dispose(cert);
return;
}
// Here's a screenshot showing the key ID of a private key in AWS KMS:
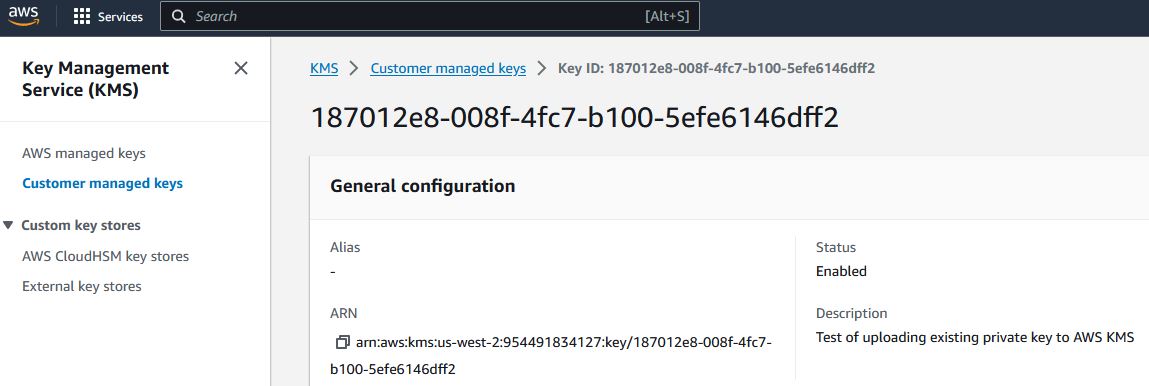 // To sign using AWS KMS,
// add the following lines of code to specify your AWS authentication credentials,
// and the ID of the KMS private key.
jsonAwsKms = CkJsonObject_Create();
// Set the "service" equal to "aws_kms" to tell Chilkat to use AWS KMS for signing.
CkJsonObject_UpdateString(jsonAwsKms,"service","aws_kms");
CkJsonObject_UpdateString(jsonAwsKms,"access_key","ACCESS_KEY");
CkJsonObject_UpdateString(jsonAwsKms,"secret_key","SECRET_KEY");
// Make sure to specify the correct region for your case.
CkJsonObject_UpdateString(jsonAwsKms,"region","us-west-2");
// In the above screenshot, our key ID is "187012e8-008f-4fc7-b100-5efe6146dff2". You will use your key ID.
CkJsonObject_UpdateString(jsonAwsKms,"key_id","187012e8-008f-4fc7-b100-5efe6146dff2");
success = CkCert_SetCloudSigner(cert,jsonAwsKms);
crypt = CkCrypt2_Create();
success = CkCrypt2_SetSigningCert(crypt,cert);
if (success == FALSE) {
printf("%s\n",CkCrypt2_lastErrorText(crypt));
CkCert_Dispose(cert);
CkJsonObject_Dispose(jsonAwsKms);
CkCrypt2_Dispose(crypt);
return;
}
// The CadesEnabled property applies to all methods that create PKCS7 signatures.
// To create a CAdES-BES signature, set this property equal to true.
CkCrypt2_putCadesEnabled(crypt,TRUE);
CkCrypt2_putHashAlgorithm(crypt,"sha256");
signedAttrs = CkJsonObject_Create();
CkJsonObject_UpdateInt(signedAttrs,"contentType",1);
CkJsonObject_UpdateInt(signedAttrs,"signingTime",1);
CkJsonObject_UpdateInt(signedAttrs,"messageDigest",1);
CkJsonObject_UpdateInt(signedAttrs,"signingCertificateV2",1);
CkCrypt2_putSigningAttributes(crypt,CkJsonObject_emit(signedAttrs));
// You can sign any type of file..
inputXmlPath = "qa_data/e-Invoice.xml";
outputP7mPath = "qa_output/signed.p7m";
// Create the CAdES-BES attached signature, which contains the original data.
// Chilkat will build the .p7m locally, but will (internally) use ARSS
// to do the RSA signing remotely.
success = CkCrypt2_CreateP7M(crypt,inputXmlPath,outputP7mPath);
if (success == FALSE) {
printf("%s\n",CkCrypt2_lastErrorText(crypt));
CkCert_Dispose(cert);
CkJsonObject_Dispose(jsonAwsKms);
CkCrypt2_Dispose(crypt);
CkJsonObject_Dispose(signedAttrs);
return;
}
printf("Success.\n");
CkCert_Dispose(cert);
CkJsonObject_Dispose(jsonAwsKms);
CkCrypt2_Dispose(crypt);
CkJsonObject_Dispose(signedAttrs);
}
// To sign using AWS KMS,
// add the following lines of code to specify your AWS authentication credentials,
// and the ID of the KMS private key.
jsonAwsKms = CkJsonObject_Create();
// Set the "service" equal to "aws_kms" to tell Chilkat to use AWS KMS for signing.
CkJsonObject_UpdateString(jsonAwsKms,"service","aws_kms");
CkJsonObject_UpdateString(jsonAwsKms,"access_key","ACCESS_KEY");
CkJsonObject_UpdateString(jsonAwsKms,"secret_key","SECRET_KEY");
// Make sure to specify the correct region for your case.
CkJsonObject_UpdateString(jsonAwsKms,"region","us-west-2");
// In the above screenshot, our key ID is "187012e8-008f-4fc7-b100-5efe6146dff2". You will use your key ID.
CkJsonObject_UpdateString(jsonAwsKms,"key_id","187012e8-008f-4fc7-b100-5efe6146dff2");
success = CkCert_SetCloudSigner(cert,jsonAwsKms);
crypt = CkCrypt2_Create();
success = CkCrypt2_SetSigningCert(crypt,cert);
if (success == FALSE) {
printf("%s\n",CkCrypt2_lastErrorText(crypt));
CkCert_Dispose(cert);
CkJsonObject_Dispose(jsonAwsKms);
CkCrypt2_Dispose(crypt);
return;
}
// The CadesEnabled property applies to all methods that create PKCS7 signatures.
// To create a CAdES-BES signature, set this property equal to true.
CkCrypt2_putCadesEnabled(crypt,TRUE);
CkCrypt2_putHashAlgorithm(crypt,"sha256");
signedAttrs = CkJsonObject_Create();
CkJsonObject_UpdateInt(signedAttrs,"contentType",1);
CkJsonObject_UpdateInt(signedAttrs,"signingTime",1);
CkJsonObject_UpdateInt(signedAttrs,"messageDigest",1);
CkJsonObject_UpdateInt(signedAttrs,"signingCertificateV2",1);
CkCrypt2_putSigningAttributes(crypt,CkJsonObject_emit(signedAttrs));
// You can sign any type of file..
inputXmlPath = "qa_data/e-Invoice.xml";
outputP7mPath = "qa_output/signed.p7m";
// Create the CAdES-BES attached signature, which contains the original data.
// Chilkat will build the .p7m locally, but will (internally) use ARSS
// to do the RSA signing remotely.
success = CkCrypt2_CreateP7M(crypt,inputXmlPath,outputP7mPath);
if (success == FALSE) {
printf("%s\n",CkCrypt2_lastErrorText(crypt));
CkCert_Dispose(cert);
CkJsonObject_Dispose(jsonAwsKms);
CkCrypt2_Dispose(crypt);
CkJsonObject_Dispose(signedAttrs);
return;
}
printf("Success.\n");
CkCert_Dispose(cert);
CkJsonObject_Dispose(jsonAwsKms);
CkCrypt2_Dispose(crypt);
CkJsonObject_Dispose(signedAttrs);
}
|

